Purpose
-
The library "alpha-bs" computes the approximation to classic and fractional Black-Scholes models for European and American options, with finite difference method, spectral method, backward Euler method, BDF2 method, Crank-Nicolson method, projected LU method, and operator splitting method.
Click Here to Download the Codes
Simple Example
- Equation:
\begin{equation}
\begin{aligned}
& v_t = \frac{\sigma^2 s^2}{2} v_{ss} + (r-q) s v_s - rv, \quad (s,t) \in (0,\infty) \times (0,T],\\
& v(s,0) = g(s).
\end{aligned}
\end{equation}
- Parameters:
\begin{equation}
T =0.25, \quad r= 0.05, \quad \sigma=0.15, \quad K=50, \quad q =0, \quad S_m = 2K.
\end{equation}
- Exact solution for European options:
\begin{equation}
\begin{aligned}
& C = Se^{-q(T-t)} N(d_1) - Ke^{-r(T-t)} N(d_2), \\
& P = Ke^{-r(T-t)} N(-d_2)-Se^{-q(T-t)}N(-d_1),
\end{aligned}
\end{equation}
where
\begin{equation} \label{x1}
d_1 = \frac{\ln(S/K) +(T-t)(r-q+\frac{\sigma^2}{2})}{\sigma \sqrt{(T-t)}}, \quad d_2 = d_1 -\sigma \sqrt{(T-t)}.
\end{equation}
In the above, $S$ is the stock price, $K$ is the strike price, $r$ is the interest rate, $q$ is the dividend rate, $T$ is the maturity span of the option, and $t$ is the spot time (e.g., $t=0$ indicates the present time).
And $N(x)$ is the cumulative distribution function (cdf) of a standard normal random variable:
\begin{equation} \label{Nx}
N(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}} \int_{-\infty}^x e^{-\frac{s^2}{2}} ds.
\end{equation}
Quick Start
- Compiling and running:
matlab test_bs_eu
- Example Output for American options:
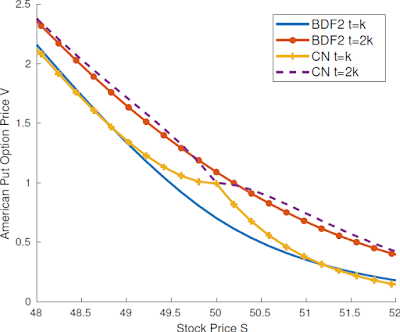
- CPU: Intel(R) i5-4310U.
- OS: Windows Home 10.
- Release: MATLAB R2017b.
References
-
A new operator splitting method for American options under fractional black–scholes models
Chris Chen, Zeqi Wang, Yue Yang,
Computers & Mathematics with Applications 77 (8), 2130-2144, 2019
-
A new spectral element method for pricing European options under the Black–Scholes and Merton jump diffusion models,
Feng Chen, Jie Shen, Haijun Yu,
Journal of Scientific Computing 52 (3), 499-518, 2012
-
Operator splitting methods for American option pricing,
Samuli Ikonen, Jari Toivanen,
Applied mathematics letters 17 (7), 809-814
Code Highlights
% Backward Euler's method for the Black-Scholes Eqaution
[v vq] = mch_bs_eu_be(pid, N, M, M, K, T, r, sigma, q, S, g, Sq);
% BDF2 method for the Black-Scholes Eqaution
[v vq] = mch_bs_eu_bdf2(pid, N, M, K, T, r, sigma, q, S, g, Sq);
% Crank-Nicolson method for the Black-Scholes Eqaution
[v vq] = mch_bs_eu_cn(pid, N, M, 4, K, T, r, sigma, q, S, g, Sq);


